What is ADSR?
ADSR, an acronym for Attack, Decay, Sustain, and Release, is a fundamental concept in music production and synthesis. It's a model used to shape and control the sound of a musical note or sound sample over time. This article will explore each component of ADSR in detail.
Introduction to ADSR
The ADSR model is a way of breaking down and understanding the complex dynamics of sound. It's a tool used in synthesizers, samplers, and digital audio workstations (DAWs) to shape the amplitude (volume) of a sound over time. By adjusting the parameters of Attack, Decay, Sustain, and Release, you can drastically alter the character of a sound.
Understanding the components of ADSR
ADSR is made up of four components: Attack, Decay, Sustain, and Release. Each component represents a different phase in the life of a sound, from the moment it begins to the moment it ends. By manipulating these components, you can shape the dynamics of a sound in various ways.
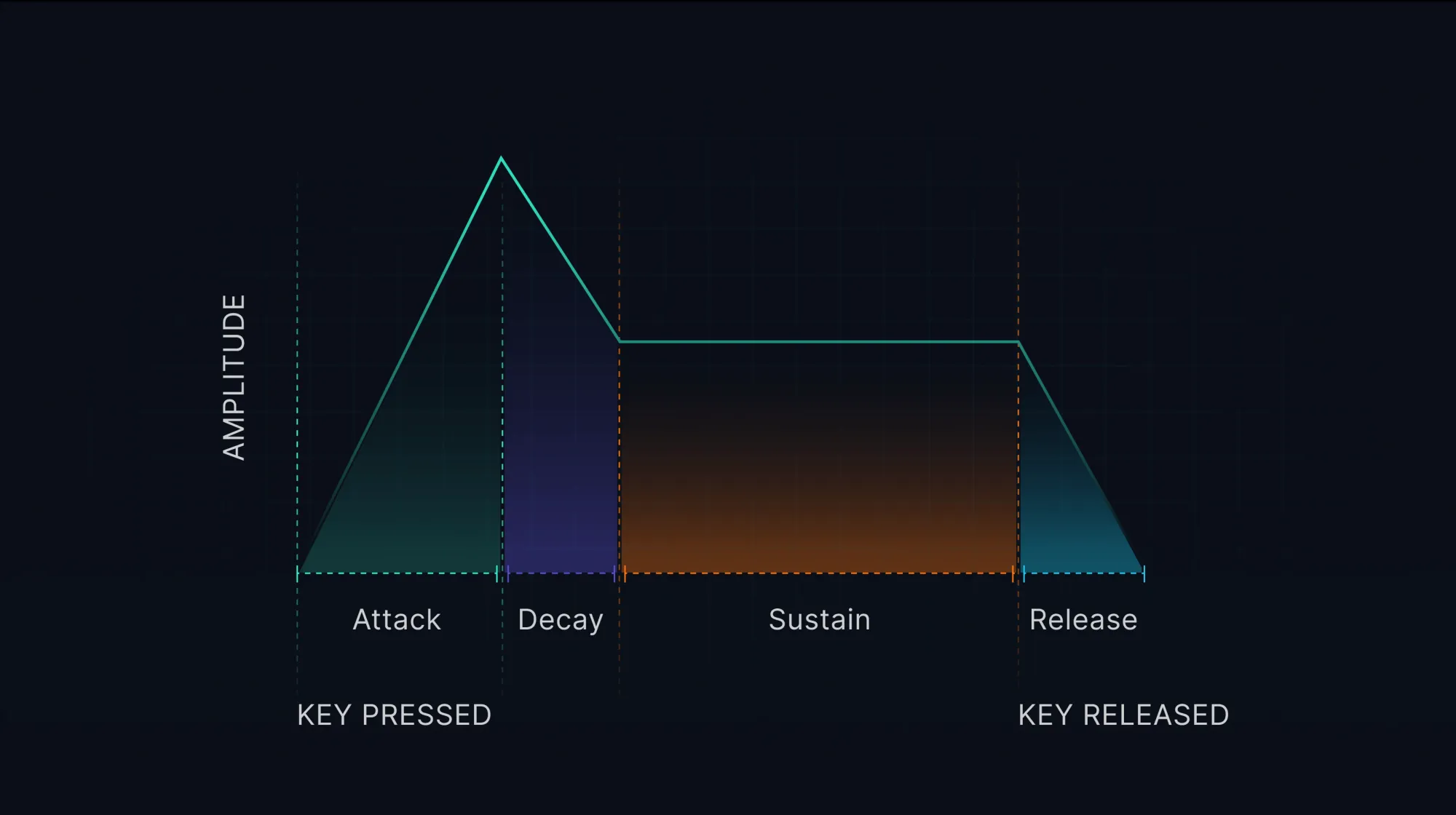
Attack
The Attack phase of ADSR represents the time it takes for a sound to reach its maximum level after it's triggered. This could be the time it takes for a piano key to be struck and reach its loudest point, or the time it takes for a synthesized sound to reach its peak.
Adjusting the Attack parameter in a synthesizer or DAW can have a dramatic effect on the sound. A short Attack time will make the sound start abruptly, while a long Attack time will make it fade in slowly. This can be used to create a variety of effects, from percussive hits to slow, evolving pads.


Decay
The Decay phase represents the time it takes for the sound to fall from its peak level to the level of the Sustain phase. This is the period of time after the initial Attack where the sound begins to settle into its sustained level. The length of the Decay phase can influence the perceived "weight" or "body" of a sound.
By adjusting the Decay parameter, you can control how quickly or slowly the sound falls to its sustained level. A short Decay time will make the sound drop quickly, creating a percussive or plucked effect. A long Decay time, on the other hand, will make the sound fall slowly, creating a more gradual transition to the Sustain phase.


Sustain
The Sustain phase represents the level at which the sound is held after the Decay phase, while the note is still being held or the sound is still being triggered. This is not a measure of time but of level. The Sustain level can greatly influence the perceived "length" or "sustain" of a sound.
By adjusting the Sustain parameter, you can control the level at which the sound is held. A high Sustain level will make the sound hold at a high volume, creating a strong, sustained sound. A low Sustain level, on the other hand, will make the sound hold at a low volume, creating a softer, more subdued sound.


Release
The Release phase represents the time it takes for the sound to fall from the Sustain level to silence after the note is released or the sound is no longer being triggered. This is the "tail" of the sound, and it can greatly influence the perceived "length" or "reverb" of a sound.
By adjusting the Release parameter, you can control how quickly or slowly the sound fades out. A short Release time will make the sound stop abruptly, while a long Release time will make it fade out slowly. This can be used to create a variety of effects, from short, staccato notes to long, reverb-like tails.









